This 3D pipeline was conducted to showcase advanced rendering techniques that could potentially be used to achieve certain effects in real-time interactive applications. I will explain several scenes that were specifically created to showcase different techniques: Deferred Lighting with Bloom and animated lights, Cascaded Shadow Maps with PCF for Directional Lights, Decal Rendering and Ambient Oclussion with Bilateral Filtering. Finally I conducted a personal project on a POSTECH paper for Real-Time Pencil Rendering that I embedded in the pipeline.
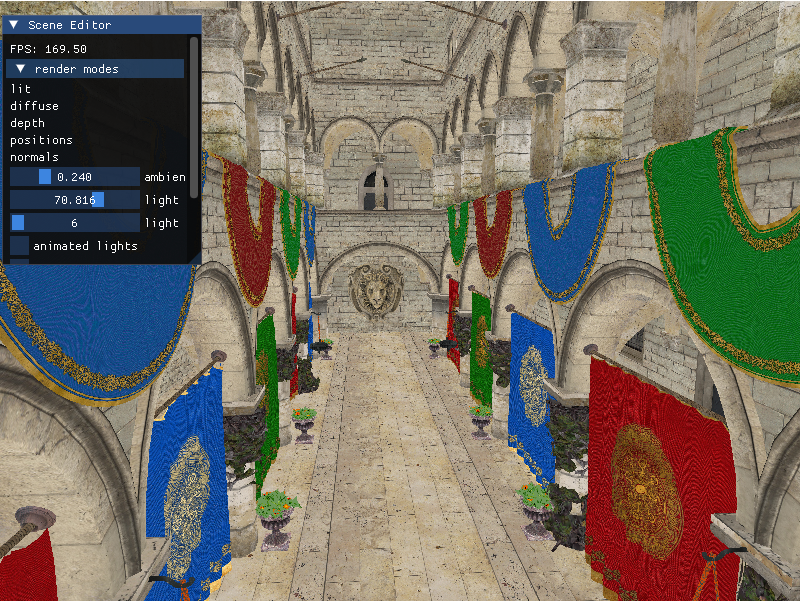
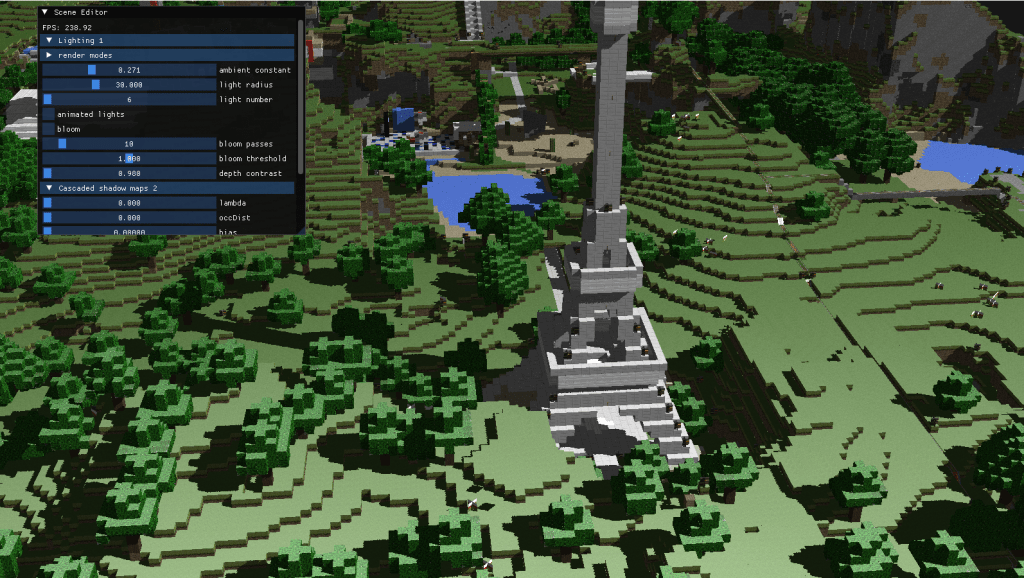
1-sponza: deferred rendering with animated lights and bloom
This first part of the project consisted on creating the pipeline from scratch and integrating deferred rendering in the system. First I built the parser that read, interpreted and stored the geometry from the .gltfs that comprised the scene. I created all the data structures that were needed to translate that information into images using a camera, meshes and vertices mainly. I programmed a camera that allowed me to freely move through the scene to test everything. Once the geometry was correctly loaded I started building the Deferred Rendering System.
Deferred Rendering is a technique that is used to optimize a scene when it has many lights. By storing the information of the geometry in the G-Buffer we can use the data in a much more optimized way. Furthermore, with the sphere optimization that I used with the lights instead of traversing each and every pixel of the screen each one just checks the area that corresponds to it’s radius.
Once I had Deferred Rendering it was a matter of adding Bloom in a modular way. For this I followed a Gaussian Blur algorithm that used Frame Buffer Ping-Poning to generate a bloomed image from the brilliance extracted in the original scene.
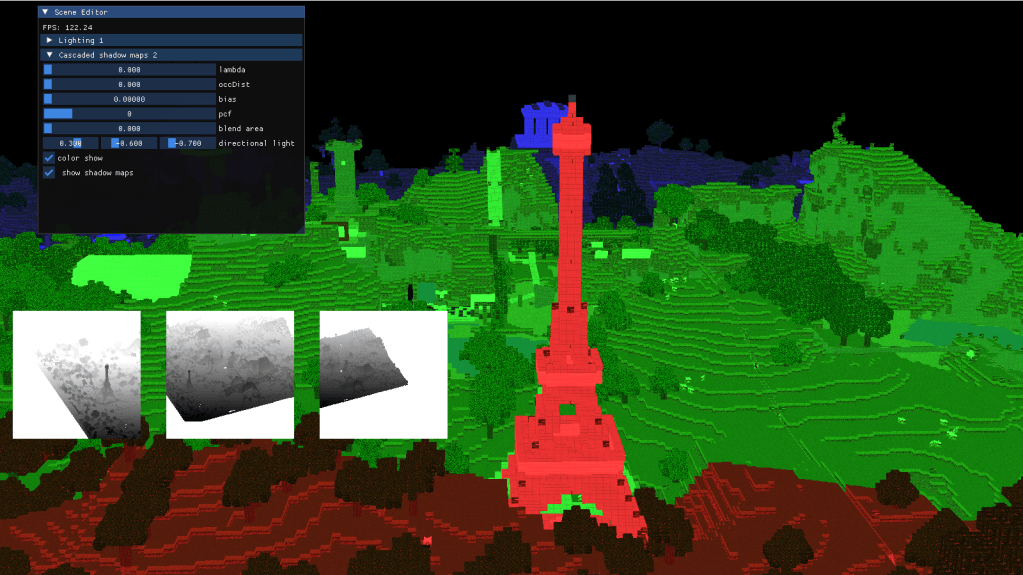
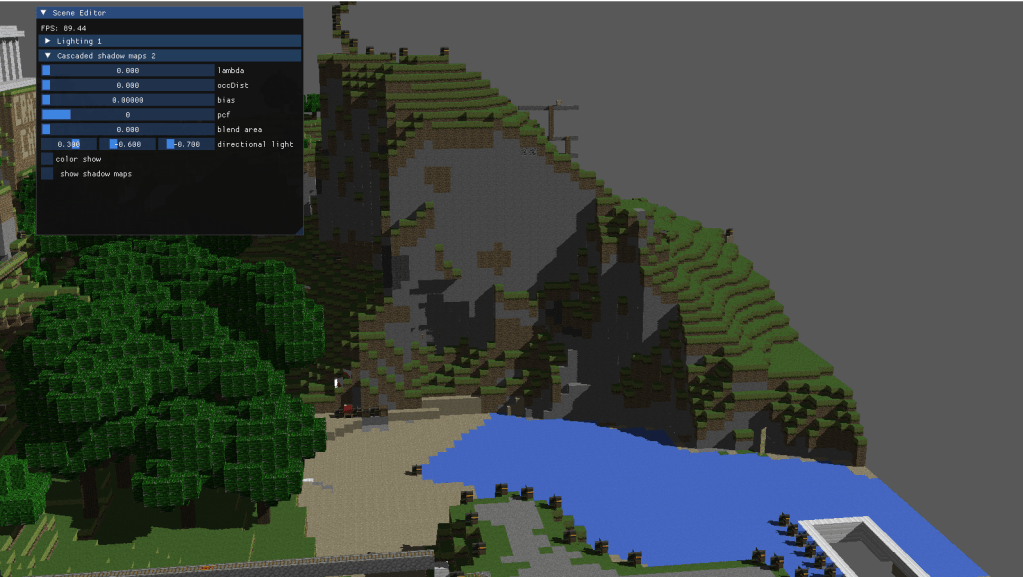
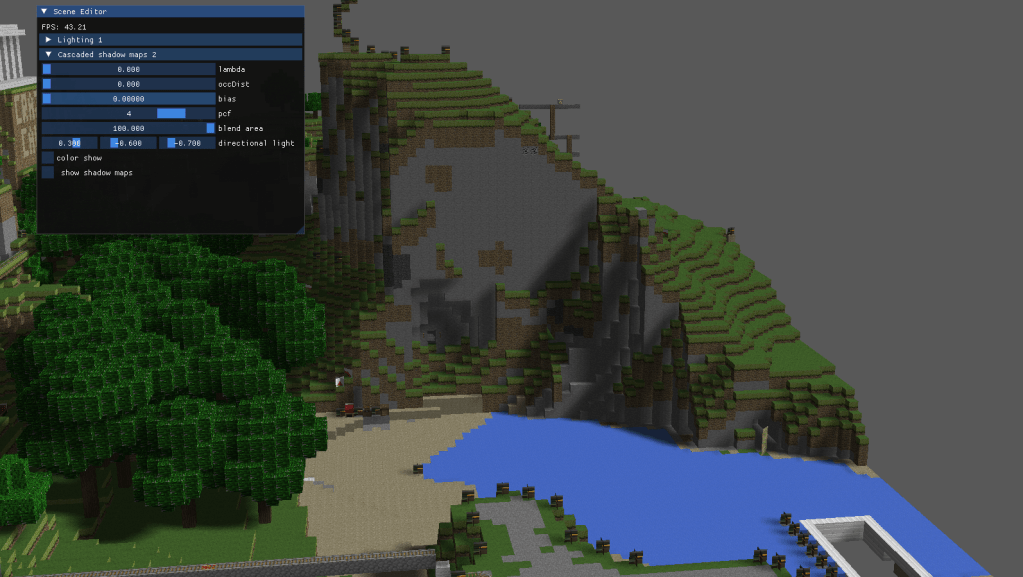
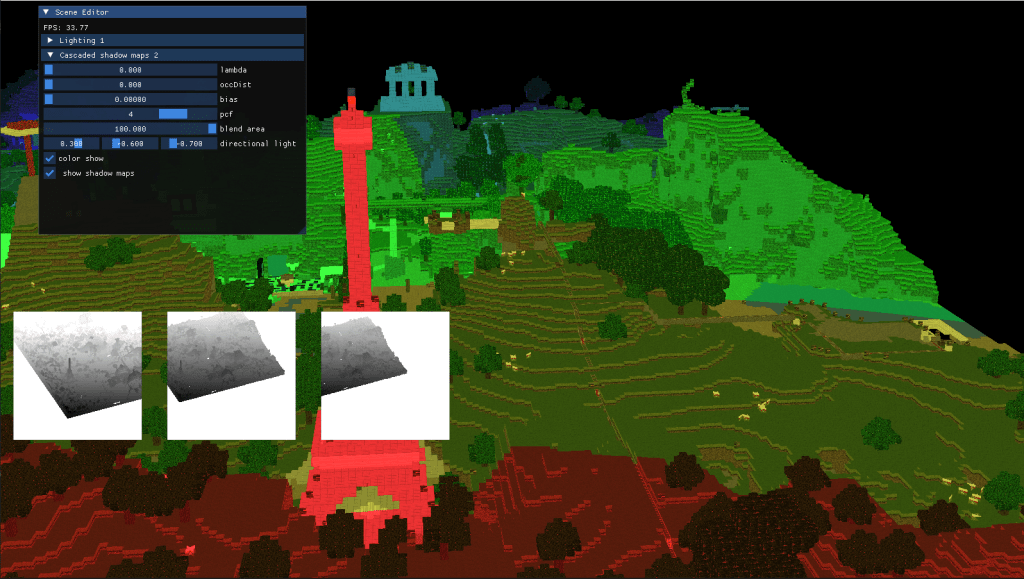
2-Vokselia: cascaded shadow maps with pcf for directional lights
During the second part of the project I implemented optimized shadowing. For big scenes and specially for directional lights shadowing everything using a shadow map of the same resolution is usually not the best idea. Generally, areas that are further away from the camera don’t require great resolutions, since they will be less relevant to the visual output.
Taking this into account I generated different shadow maps from the lights perspective using an orthogonal view matrix, and later extracted the shadows from the respective cascade. To choose the shadow maps and the cascades I added a variable threshold parameter that changed the way in which the cascades are split, changing from linear to logaritmic.
Finally, to elevate the quality of the shadows and avoid artifacts I added an oclussion bias that prevents the shadows from being truncated by the light volume. On the same note I added Percentage Close Filtering to soften the edges of the shadows and I allowed blending between the cascades, so that the resolution change is less noticeable.
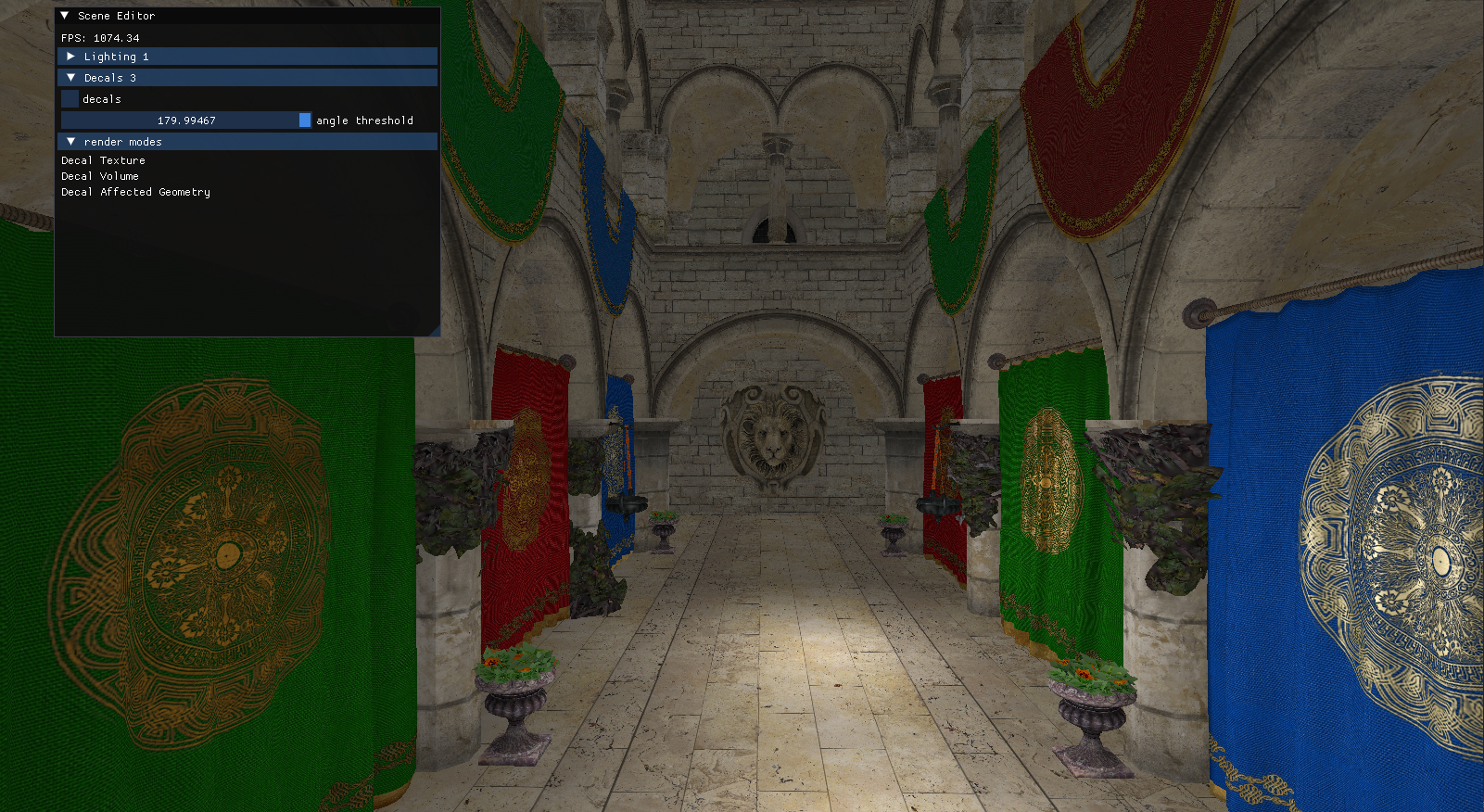
3-sponza: decal rendering and mapping
Decals are materials projected onto surfaces in the world — like virtual stickers or paint splashes that don’t affect the underlying geometry, but still appear visually stuck to it.
For this part of the pipeline I basically projected these materials onto different surfaces. The approach that I followed was to use the data of the G-Buffer to determine how the decal should appear. I programmed a new pass in the pipeline that used decal volumes to calculate the intersection between the decal and the geometry. Once calculated, I did the necessary transformations and mapped them from screen space to the desired position.

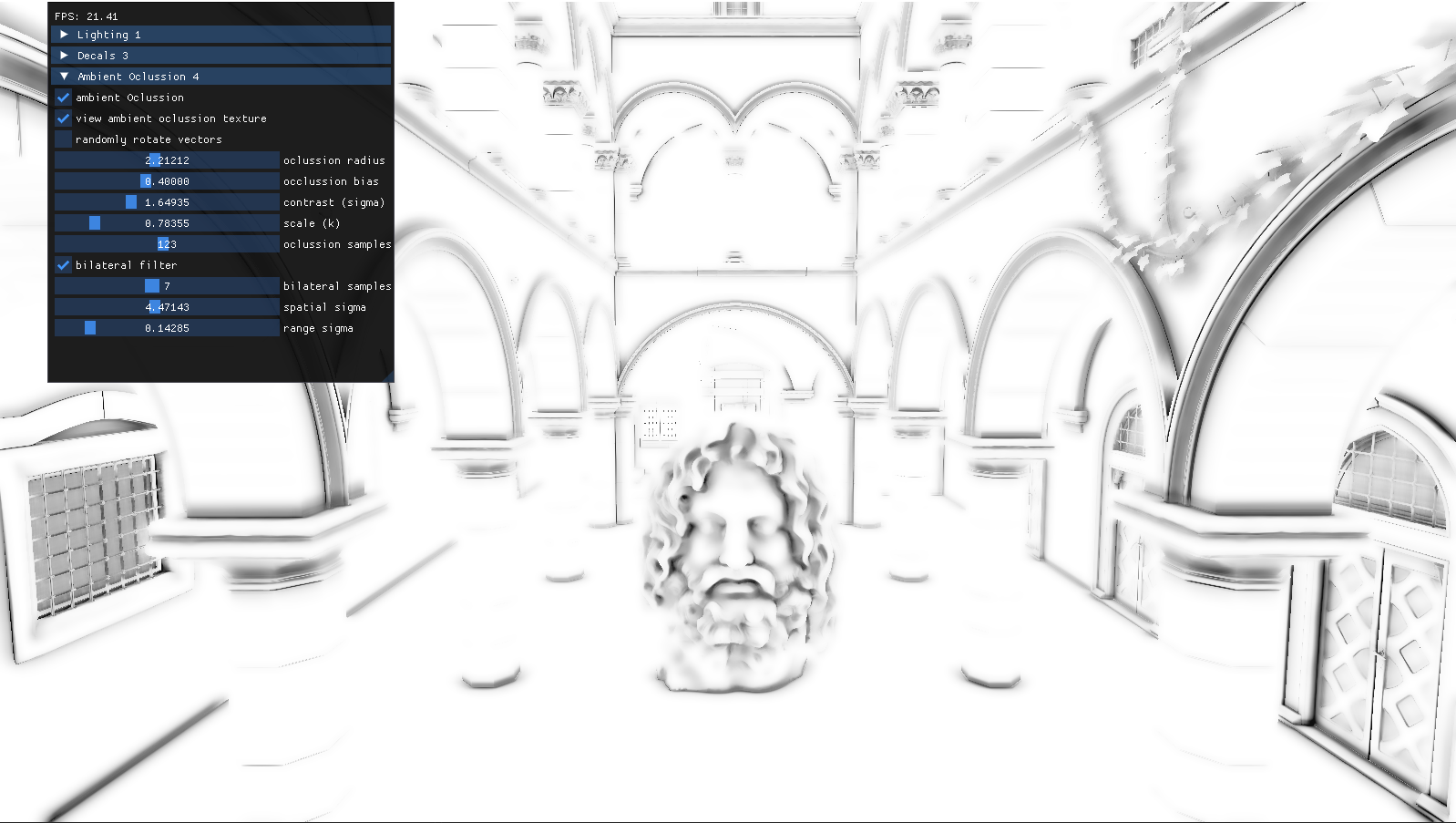
4-sponza: ambient oclussion with bilateral filtering
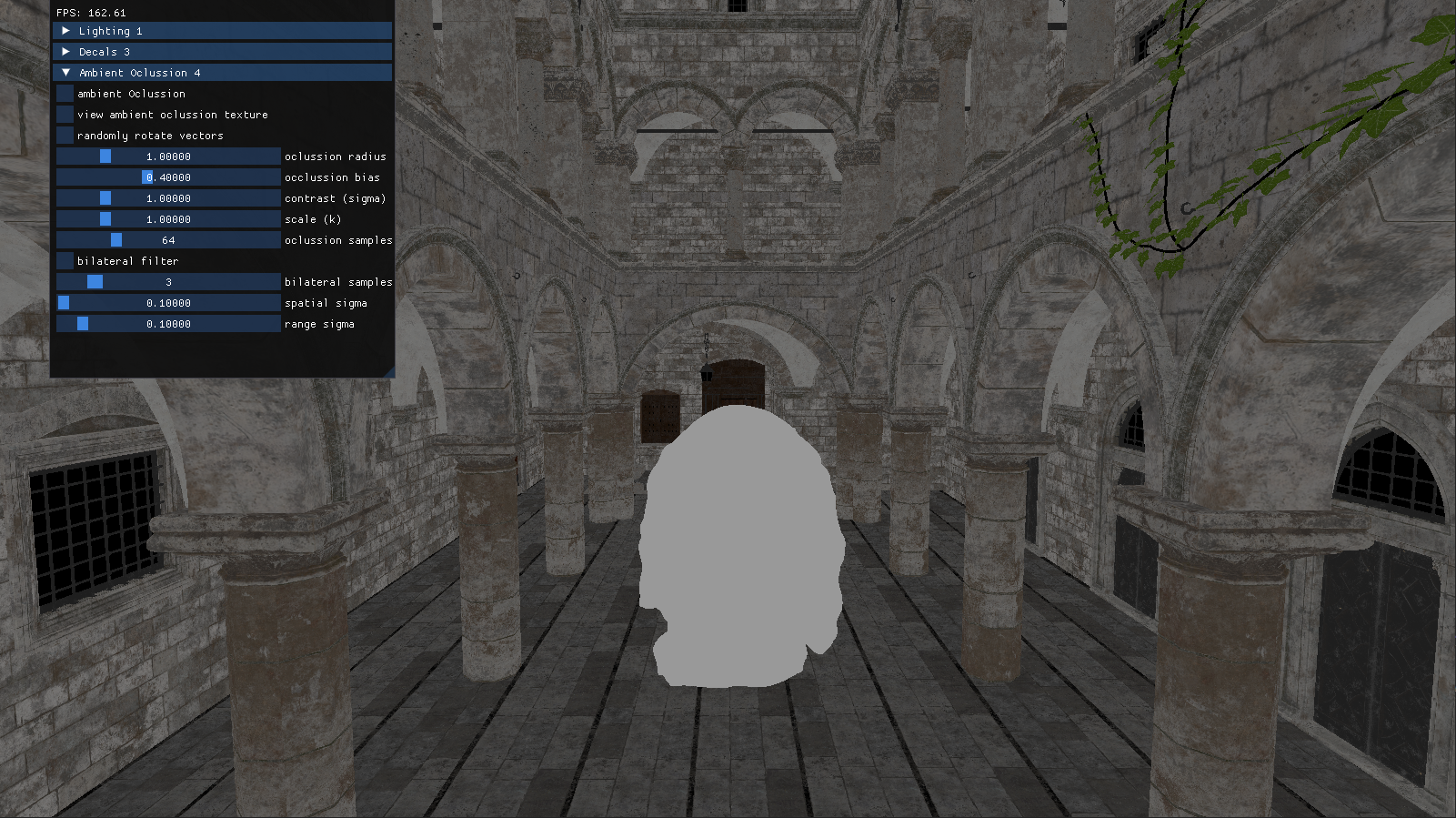
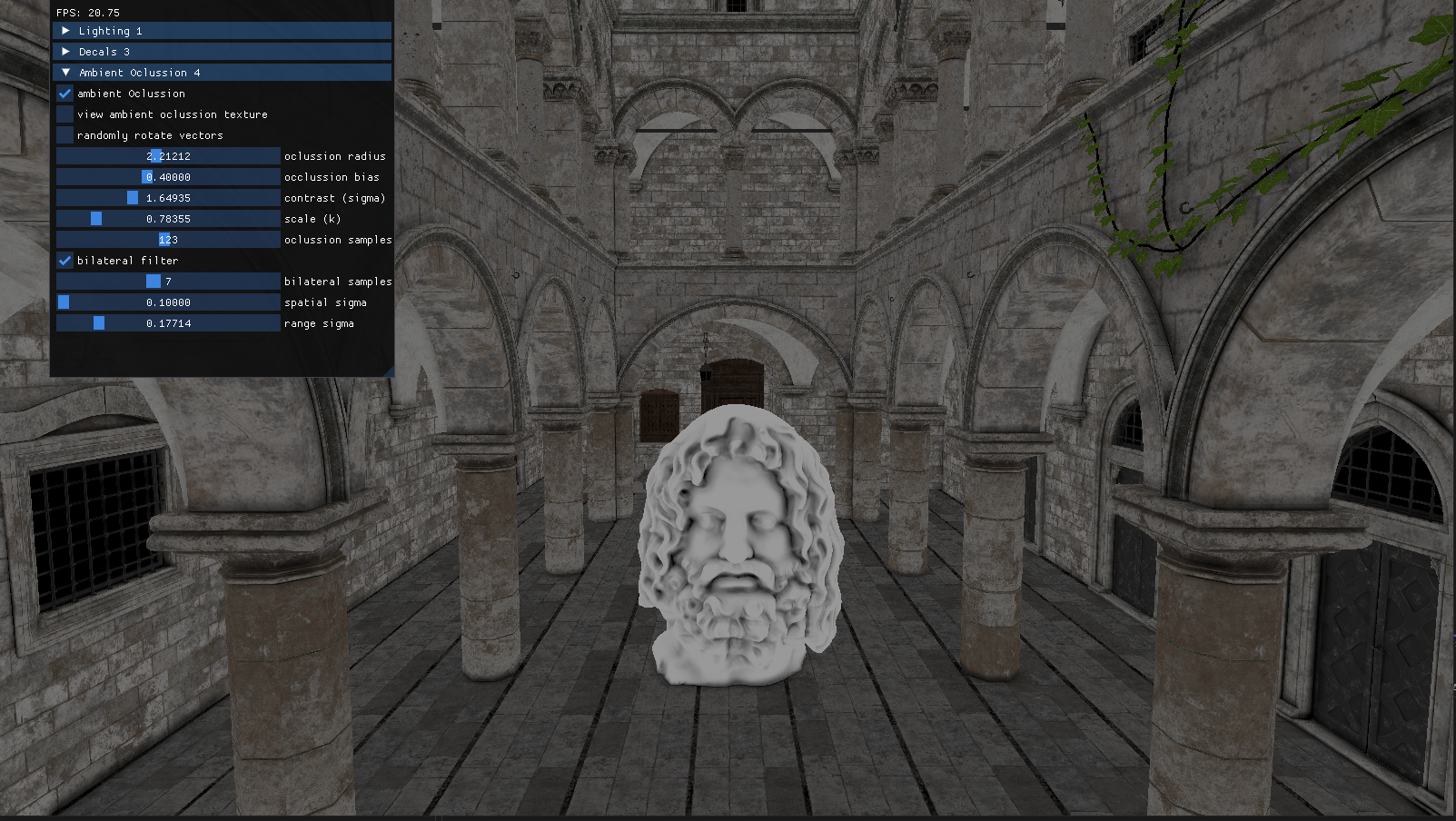
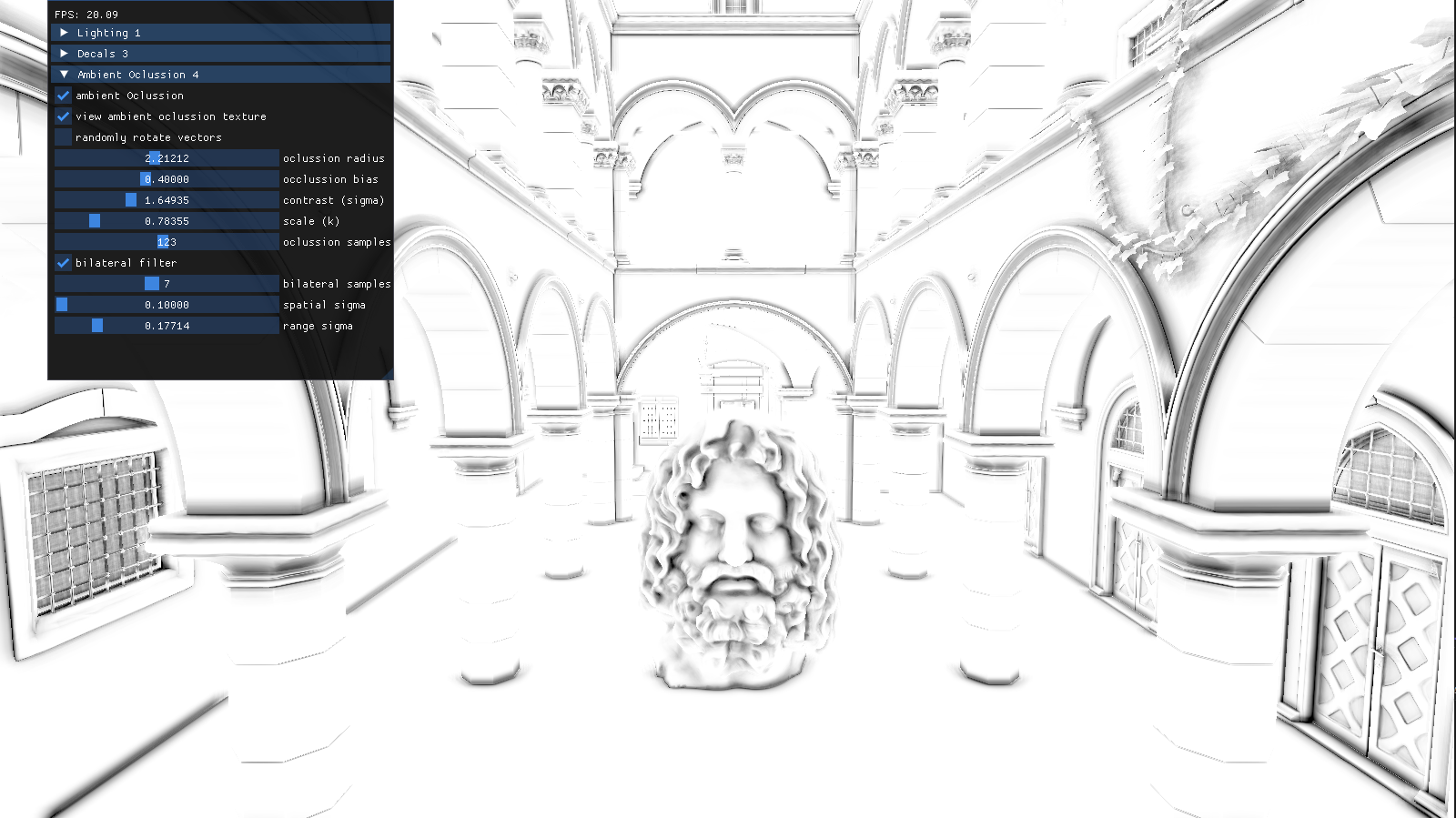
The final part of the project consisted in adding Alchemy Ambient Oclussion with Bilateral Filtering to the scene. Ambient Oclussion is a shading and rendering technique used to simulate how light behaves in real-world environments, specifically how it is blocked or occluded in areas where objects are close together.
This algorithm adds a new pass that uses Alchemy AO to occlude the parts of the geometry that would naturally be darker. It relies on a screen space area to calculate the difference of depth in the neighbouring geometry to determine the grade of oclussion in the pixel.
Bilateral Filter is used to blur and attenuate the dark areas without losing precision on the edges of the geometry.
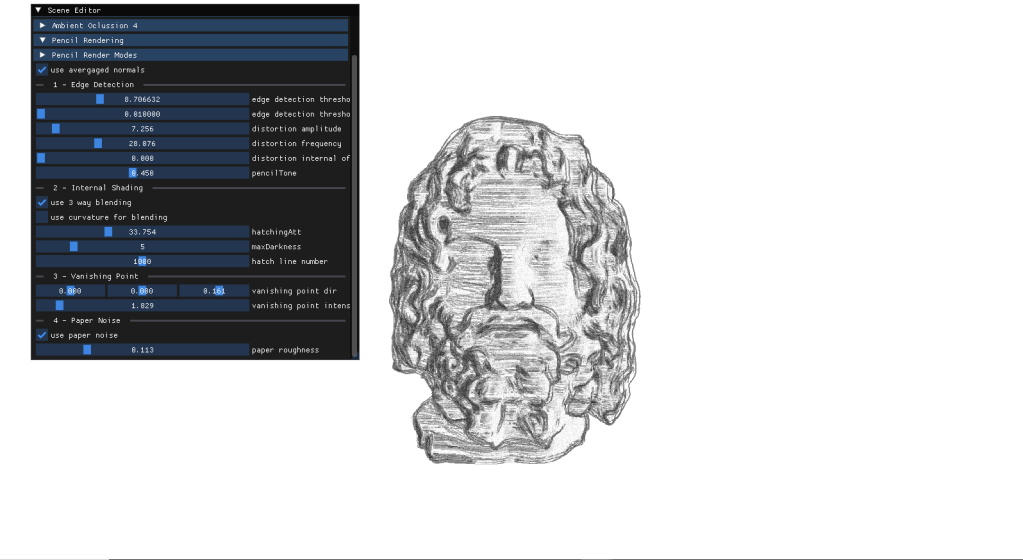
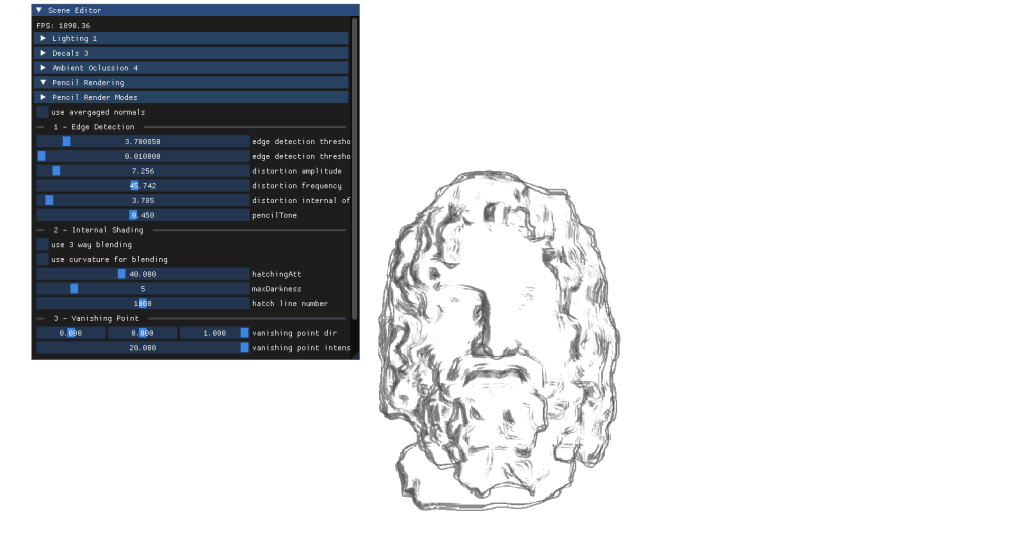
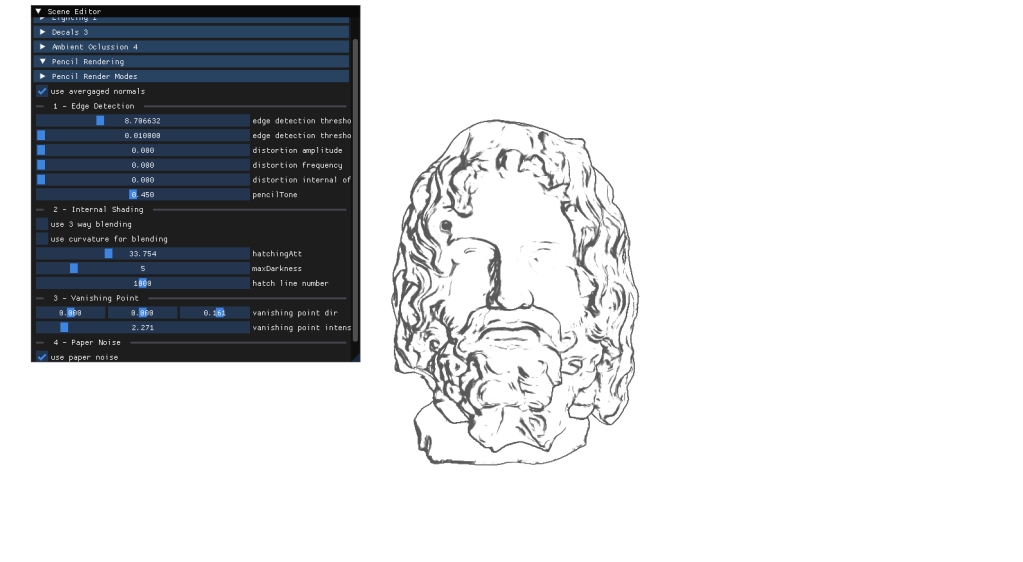
5- pencil rendering
For my final project I had to implement a personal approach on a paper of my choice. After carefully thinking about it I chose to deliver an approach for Real-Time Pencil Rendering, based on the initial proposition conducted by POSTECH in 2006 that carefully explained their approach on how to render geometry in a way that it simulated human-drawn patterns.
For more information about my project I wrote a memoir myself, reflecting on the journey interpreting the previously mentioned paper and my problems during the implementation, as well as the conclussions on the method. Here you can find it: